Page 38 - CII ARTHA
P. 38
ARTHA
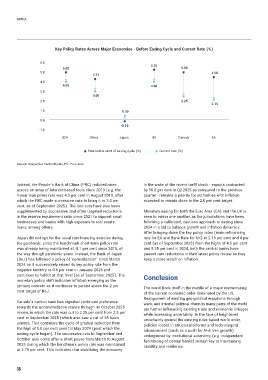
Key Policy Rates Across Major Economies - Before Easing Cycle and Current Rate (%)
6.0 5.25
5.00 5.00
5.0 4.50
4.31
4.0
4.00 4.00
3.0
3.00
2.0 2.25
2.15
1.0 0.50
0.0
-0.10
-1.0
USA China Japan UK Canada EA
Rate before start of easing cycle (%) Current rate (%)
Source: Respective Central Banks; EA - Euro Area
Instead, the People’s Bank of China (PBC) reduced rates in the wake of the recent tariff shock - exports contracted
across an array of interest-based tools since 2019 (e.g. the by 10.8 per cent in Q2:2025 as compared to the previous
1-year loan prime rate was 4.3 per cent in August 2019, after quarter - remains a priority for authorities with inflation
which the PBC made successive cuts to bring it to 3.0 per expected to remain close to the 2.0 per cent target.
cent, as of September 2025). The rate cuts have also been
supplemented by successive, and often targeted reductions Monetary easing for both the Euro Area (EA) and the UK is
in the reserve requirement ratio since 2021 to support small seen to mirror one another, as the jurisdictions have been
businesses and banks with high exposure to real estate following a calibrated, cautious approach to easing since
loans, among others. 2024 in a bid to balance growth and inflation dynamics.
After bringing down the key policy rates (main refinancing
Japan did not opt for the usual rate-lowering exercise during rate for EA and Bank Rate for UK) to 2.15 per cent and 4 per
the pandemic, since the benchmark short-term policy rate cent (as of September 2025) from the highs of 4.5 per cent
was already being maintained at -0.1 per cent since 2016, all and 5.25 per cent in 2024, both the central banks have
the way though pandemic years. Instead, the Bank of Japan paused rate reductions in their latest policy review as they
(BoJ) has followed a policy of ‘normalization’ since March keep a close watch on inflation.
2024 as it successively raised its key policy rate from the
negative territory to 0.5 per cent in January 2025 and
continues to hold it at that level (as of September 2025). The Conclusion
monetary policy shift indicates inflation emerging as the
primary concern as it continues to persist above the 2 per The world finds itself in the middle of a major restructuring
cent target of BoJ. of the current economic order dominated by the US.
Realignment of existing geo-political equations through
Canada’s central bank has signaled continued preference wars, and internal political churn in many parts of the world
towards the accommodative stance through its October 2025 are further influencing existing trade and economic linkages
review, in which the rate was cut to 2.25 per cent from 2.5 per while increasing uncertainty. In the face of heightened
cent in September 2025 (which also saw a cut of 25 basis uncertainty around the existing rules-based world order,
points). This continues the cycle of gradual reduction from policies rooted in structural reforms and technological
the high of 5.0 per cent seen till May 2024 (post which the advancement (such as a push for AI-driven growth),
easing cycle began). The successive cuts in September and underpinned by institutional autonomy (e.g. independent
October also come after a short pause from March to August functioning of central banks) remain key to maintaining
2025 during which the benchmark policy rate was maintained stability and resilience.
at 2.75 per cent. This indicates that stabilizing the economy
38