Page 9 - CII ARTHA
P. 9
OCTOBER 2025
Jobs and Trade Reform Tariff cuts, ideally in the context of broader trade agreements
that expand market access, would lift, but also shift,
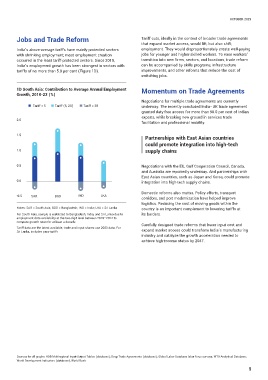
India’s above-average tariffs have mainly protected sectors employment. They would disproportionately create well-paying
with shrinking employment; most employment creation jobs for younger and higher-skilled workers. To ease workers’
occurred in the least tariff-protected sectors. Since 2010, transition into new firms, sectors, and locations, trade reform
India’s employment growth has been strongest in sectors with can be accompanied by skills programs, infrastructure
tariffs of no more than 5.0 per cent (Figure 1D). improvements, and other reforms that reduce the cost of
switching jobs.
1D South Asia: Contribution to Average Annual Employment Momentum on Trade Agreements
Growth, 2010-23 (%)
Negotiations for multiple trade agreements are currently
Tariff < 5 Tariff (5, 20) Tariff > 20 underway. The recently concluded India–UK trade agreement
granted duty-free access for more than 90.0 per cent of Indian
exports, while breaking new ground in services trade
2.0
facilitation and professional mobility.
1.5
Partnerships with East Asian countries
could promote integration into high-tech
1.0 supply chains
0.5 Negotiations with the EU, Gulf Cooperation Council, Canada,
and Australia are reportedly underway. And partnerships with
East Asian countries, such as Japan and Korea, could promote
0.0 integration into high-tech supply chains.
Domestic reforms also matter. Policy efforts, transport
-0.5 SAR BGD IND LKA
corridors, and port modernization have helped improve
logistics. Reducing the cost of moving goods within the
Notes: SAR = South Asia; BGD = Bangladesh; IND = India; LKA = Sri Lanka country is an important complement to lowering tariffs at
For South Asia, sample is restricted to Bangladesh, India, and Sri Lanka due to its borders.
employment data availability at the two-digit level between 2010–2014 to
compute growth rates for at least a decade
Carefully designed trade reforms that lower input cost and
Tariff data are the latest available, trade and input shares use 2023 data. For expand market access could transform India’s manufacturing
Sri Lanka, includes para-tariffs
industry and catalyze the growth acceleration needed to
achieve high-income status by 2047.
Sources for all graphs: ADB Multiregional Input-Output Tables (database); Deep Trade Agreements (database); Global Labor Database labor force surveys; WTO Analytical Database;
World Development Indicators (database), World Bank
9